WS Protocol
WS Protocol
Introduction
Zilla implements WebSockets (WS) as a protocol binding, designed to enable full-duplex, low-latency communication between clients and servers in distributed environments. This empowers Zilla to support real-time, event-driven interactions, making it ideal for applications such as live notifications, collaborative tools, and interactive web experiences that demand persistent, high-performance connections.
WS Communication
The WebSocket protocol enables ongoing, full-duplex, bidirectional communication between a web client and a web server over an underlying TCP connection. The protocol is designed to allow clients and servers to communicate in realtime, allowing for efficient and responsive data transfer in web applications.
WS Communication Workflow
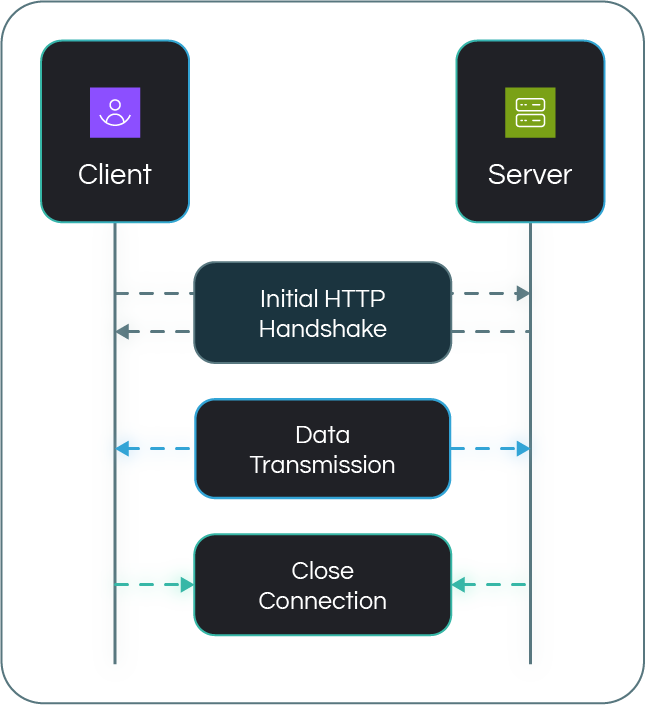
Here's a step-by-step explanation of how WebSocket works:
Connection initiation - The client and the server initiate the process of establishing a WebSocket connection through an opening handshake, which consists of an
HTTP/1.1 requestandresponseexchange.Here is an example of the HTTP request and response for WebSocket connection initiation:
GET /chat HTTP/1.1 Host: example.com Connection: Upgrade Upgrade: websocket Sec-WebSocket-Key: dGhlIHNhbXBsZSBub25jZQ== Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13HTTP/1.1 101 Switching Protocols Upgrade: websocket Connection: Upgrade Sec-WebSocket-Accept: s3pPLMBiTxaQ9kZCZrXkE9s7wE3R4Kkg1s5H1YcG3uo=Data transmission - Once the connection is established, data is sent in both directions as messages; for example, the client sends a message like
{"action": "sendMessage", "content": "Hello"}and the server responds with{"status": "ok", "messageId": 123}.Connection termination - Either the client or server initiates the closing handshake, sending a close frame to gracefully terminate the connection, and the other party acknowledges the closure; for example, the client sends
{"action": "close"}, and the server responds with{"status": "closed"}.
WS Frame Structure
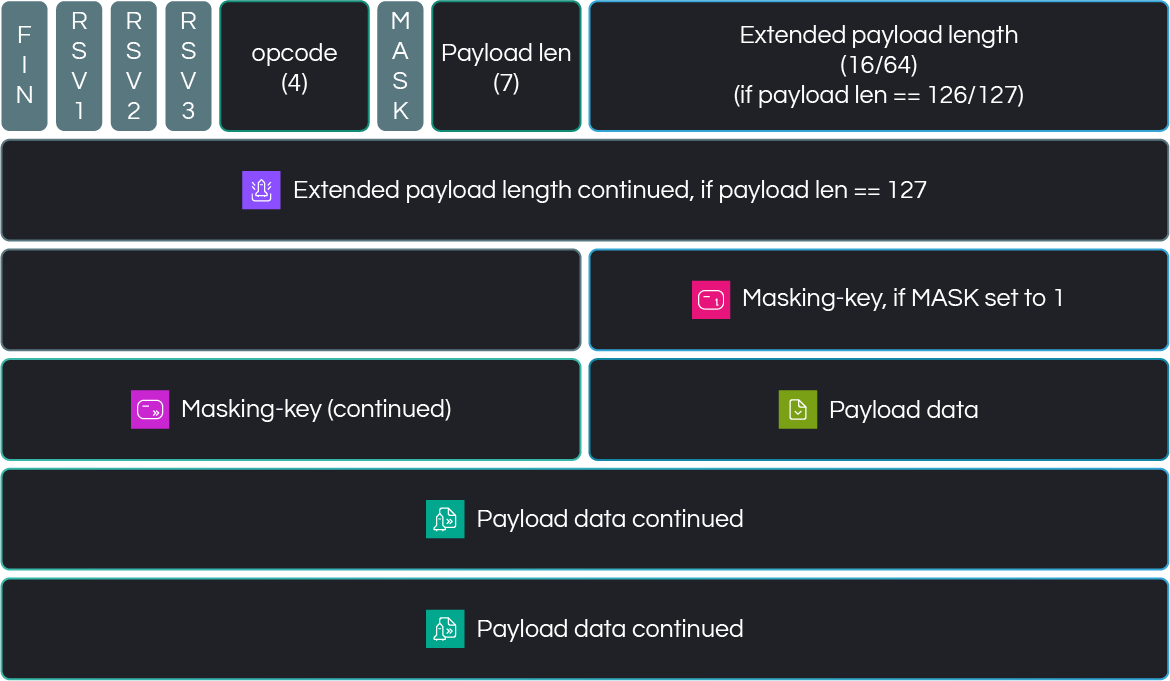
The WebSocket frame structure consists of several components:
- Metadata Headers—Information about the frame (FIN, RSV1, RSV2, RSV3, Opcode, Mask, Payload Length, and Masking Key).
- Payload Data (variable size) – The actual message content, either text or binary.
Security
Securing WS with TLS
WebSocket is a communication protocol that enables real-time, bidirectional data exchange between clients and servers. To ensure secure transmission, WebSocket can operate over TLS (Transport Layer Security) using WSS (WebSocket Secure), which encrypts data and protects against unauthorized interception, data tampering, and man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks.
Zilla provides support for TLS bindings to enforce secure communication between WebSocket clients and servers, ensuring that all messages are encrypted in transit and protected from unauthorized access or tampering.
JWT Guard
Zilla provides support for JWT Guard to enable authentication and authorization using JSON Web Tokens (JWT), ensuring that only trusted clients can access protected resources by validating token integrity and claims.
Zilla: Beyond Standard TCP
Zilla serves as an intelligent gateway for WebSocket (WS) connections, managing both inbound and outbound data streams.
- Dynamic Routing: Routes WebSocket connections based on conditions like protocol and path, ensuring traffic is directed efficiently.
- Full-Duplex Communication: Converts HTTP streams into WebSocket streams, enabling continuous two-way communication.
- Secure Connections: Integrates TLS binding for encrypted WebSocket communication, ensuring data privacy.
- Data Governance: Leverages Schema Registry for message validation, ensuring data integrity and consistent structure in WS communications.
Zilla: WS Use Cases
Zilla leverages the WebSocket protocol to provide powerful bidirectional communication, real-time event streaming, and secure data exchange, ensuring efficient and persistent connections between clients and servers.
Reference
ws Binding The ws support, with server or client behavior.

