MQTT Kafka Proxy
MQTT Kafka Proxy
Overview
The Zilla MQTT Kafka Proxy manages MQTT Pub/Sub connections and messages on and off of Kafka.
An MQTT server acts as a broker between publishers and subscribers. This requires a complex protocol to manage the wide range of IoT devices and use cases. By proxying these messages on and off of Kafka with the mqtt-kafka binding in a zilla.yaml config, IoT devices can transmit data to a wider range of tech stacks, adapting to more business needs.
Zilla uses specific Kafka topics to store and route MQTT messages, meaning the Kafka architecture can be optimized for MQTT Pub/Sub. MQTT client subscribers and publishers will communicate with Zilla the same as any broker.

MQTT Broker
A Zilla MQTT server can manage client sessions and broker all traffic, adhering to the official MQTT protocol.
Protocol versions
An MQTT client can use either the MQTT v5.0 and MQTT v3.1.1 specifications.
QOS
An MQTT client can use any Quality of Service flag.
- QoS 0 - At most once
- QoS 1 - At least once
- QoS 2 - Exactly once
MQTT over WebSocket
The tcp binding defines the ports Zilla will accept traffic for both MQTT and WebSocket connections. Zilla natively handles WebSockets and can manage the MQTT protocol over an active connection.
Last Will and Testament
An MQTT client can specify a last will and testament (LWT) message and topic that is delivered when the client disconnects abruptly and fails to reconnect before session timeout.
Correlated request-response
An MQTT client can use the v5 request-response paradigm to send messages with a response topic and correlated data. A requesting MQTT client can send a message on one topic and receive a response on another, while a responding MQTT client or any Kafka workflow can handle the message's journey.
Reconnect
An MQTT client reconnecting with the same client-id, even to a different Zilla instance, will automatically remain subscribed to MQTT topics previously subscribed while previously connected.
Session takeover
An MQTT client connecting with the same client-id, even to a different Zilla instance, will automatically disconnect the original MQTT client and take over the session.
Redirect
An MQTT client can be redirected to a specific Zilla instance, sharding client session state across Zilla instances without needing to replicate every client's session state on each Zilla instance.
Key Capabilities
Pub/Sub with Kafka
Zilla manages MQTT publish-subscribe (pub/sub) operations using Kafka, ensuring seamless message flow between MQTT clients and Kafka topics. It utilizes three Kafka topics to handle different aspects of MQTT communication, allowing for efficient data streaming and event-driven processing. The specific topic names can be configured using the options.topics property.
Messages on Kafka
All MQTT messages brokered by Zilla are published to a designated Kafka topic. The MQTT message topic is mapped as the Kafka key, enabling efficient lookup, partitioning, and message distribution. This structure ensures that messages are stored reliably and can be consumed by Kafka clients in real time.
Topic Routing
Zilla provides configurable routes to direct MQTT publish and subscribe operations to specific Kafka topics beyond the default message topic. This flexibility allows for efficient message organization while ensuring that session and retained topics remain unaffected by routing changes.
Retaining Messages
MQTT clients can publish messages with a retain flag, which ensures that a copy is stored in a dedicated retained Kafka topic. When a new subscriber joins and requests a replay-on-subscribe, Zilla delivers the retained messages from Kafka, providing a consistent experience for late-joining clients.
Session Management
Client connection states, including MQTT connect, disconnect, and subscription details, are tracked in a log-compacted Kafka topic dedicated to sessions. Each MQTT client ID is used as a key, ensuring that session information is preserved across reconnects and enabling stateful interactions.
Kafka Consumer Groups for MQTT Sessions
Zilla assigns a dedicated Kafka consumer group to each MQTT client session, following a structured naming format: zilla:<zilla namespace>-<binding name>-<MQTT client ID>. This approach optimizes session tracking while minimizing heartbeat traffic. If a client disconnects and does not reconnect within the session expiry interval, Zilla automatically cleans up the corresponding consumer group and session state in Kafka.
Use Cases
Bridging MQTT and Modern Applications
Many IoT and messaging-based systems use MQTT for lightweight, efficient communication. However, integrating MQTT with modern applications that rely on different protocols can be complex. An MQTT broker or gateway helps bridge this gap, enabling seamless communication between MQTT devices and other services.
Real-Time Data Streaming for IoT
IoT devices frequently generate real-time data that needs to be processed and distributed efficiently. By leveraging MQTT, applications can subscribe to device events, process them, and trigger actions with minimal latency. The Taxi demo illustrates this by using MQTT to stream live location updates from vehicles, enabling real-time tracking and event handling.
Examples
Access the MQTT Kafka example files here: MQTT Kafka Repository
Full MQTT kafka zilla.yaml Config
---
name: zilla-mqtt-kafka-proxy
bindings:
north_tcp_server:
type: tcp
kind: server
options:
host: 0.0.0.0
port:
- 7183
routes:
- when:
- port: 7183
exit: north_mqtt_server
north_mqtt_server:
type: mqtt
kind: server
exit: north_mqtt_kafka_mapping
north_mqtt_kafka_mapping:
type: mqtt-kafka
kind: proxy
options:
topics:
sessions: mqtt-sessions
messages: mqtt-messages
retained: mqtt-retained
clients:
- place/{identity}/#
routes:
- when:
- publish:
- topic: place/+/device/#
- topic: device/#
- subscribe:
- topic: place/+/device/#
- topic: device/#
with:
messages: mqtt-devices
exit: north_kafka_cache_client
exit: north_kafka_cache_client
north_kafka_cache_client:
type: kafka
kind: cache_client
exit: south_kafka_cache_server
south_kafka_cache_server:
type: kafka
kind: cache_server
options:
bootstrap:
- mqtt-messages
- mqtt-retained
- mqtt-devices
exit: south_kafka_client
south_kafka_client:
type: kafka
kind: client
options:
servers:
- ${{env.KAFKA_BOOTSTRAP_SERVER}}
exit: south_tcp_client
south_tcp_client:
type: tcp
kind: client
telemetry:
exporters:
stdout_logs_exporter:
type: stdoutThe above configuration is an example of an MQTT Kafka. It listens on mqtt port 7183 and will forward mqtt publish messages from mqtt client to Kafka, delivering to all mqtt clients subscribed to the same topic.
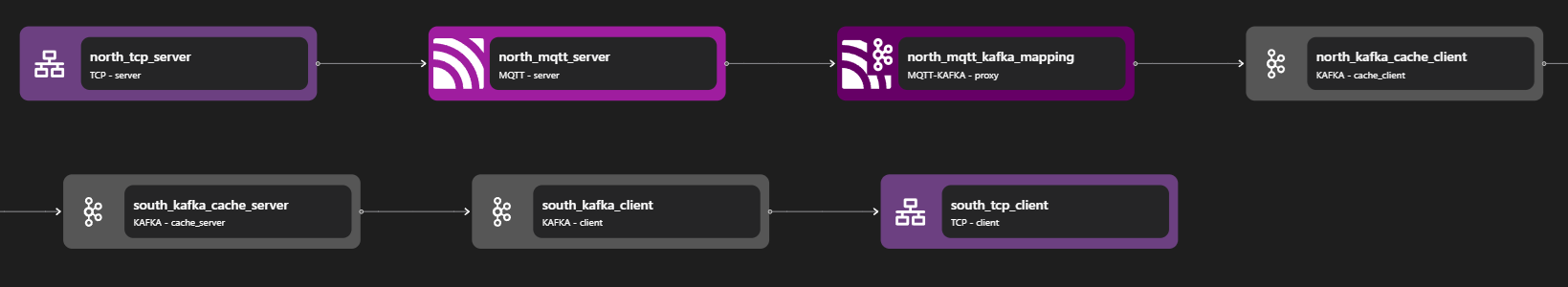
The MQTT Kafka Proxy can be constructed with three parts: the MQTT server, the MQTT-Kafka adapter, and the Kafka client. When the MQTT server receives a request, the stream is passed into an MQTT-Kafka adapter and then converted into a Kafka request.
The MQTT server consists of the following bindings: TCP Server, TLS Server (Optional), and MQTT server. A TCP Server is required to open a specific port and allow inbound connections. A TLS server is optional but can be used to perform TLS encryption for MQTTS. The data stream is then passed to the MQTT server.
The Kafka client consists of the following bindings: Kafka Cache Client, Kafka Cache Server, Kafka Client, and TCP Client. A TCP client is required to allow outbound TCP connections and a Kafka Client is used to connect to external Kafka services. Kafka Cache Client and Server are used for additional layers before direct connection to the Kafka client. These bindings add a caching layer and additional features to Kafka requests through Zilla.
The MQTT-Kafka adapter is used to convert MQTT-based requests into Kafka-based requests.

