SSE Kafka Proxy
SSE Kafka Proxy
Overview
Zilla's SSE-Kafka Proxy provides a seamless binding between Server-Sent Events (SSE) and Kafka, enabling SSE APIs to interact with Kafka’s event-driven architecture. It simplifies integration by allowing SSE clients to consume Kafka messages over HTTP, ensuring efficient real-time streaming with reliability, scalability, and flexible message filtering.

Key Capabilities
Protocol Adaptation
The SSE-Kafka Proxy facilitates seamless integration between Server-Sent Events (SSE) and Kafka. It enables the adaptation of SSE data streams into Kafka data streams, allowing Kafka messages to be delivered to SSE clients over standard HTTP connections.
Message Filtering
The proxy supports filtering Kafka messages based on message keys, headers, or a combination of both. This feature ensures that clients receive only relevant data, optimizing network usage and enhancing performance by reducing unnecessary data transmission.
Reliable Delivery
Progress across Kafka topic partitions is conveyed to the SSE client via event id. When the stream is interrupted due to an SSE client reconnect, the last-event-id header in the reconnect request contains the last received event ID. This enables the SSE stream to resume seamlessly, ensuring no messages are lost and maintaining continuous data delivery.
Caching
The proxy can be configured to cache recent Kafka messages, enhancing efficiency and reducing the load on Kafka brokers. This allows clients that reconnect or subscribe late to access historical data without repeatedly querying Kafka.
Tombstone Message Handling
When the SSE-Kafka binding receives a Kafka tombstone (null value) message, it sends a delete event to the SSE client. The client can identify which message was deleted by referencing the message key from the SSE delete event id, ensuring accurate data synchronization.
AsyncAPI Integration
The SSE-Kafka Proxy supports integration with the AsyncAPI specification, an open-source initiative for defining asynchronous APIs. This integration enables standardized documentation and management of event-driven architectures, facilitating seamless communication and easier adoption across different services.
Use Cases
Enabling Real-Time Data Streaming Over HTTP
By adapting Kafka topics to SSE, applications can push live updates to browsers, mobile devices, and external systems using a simple HTTP connection.
Simplifying Integration Between SSE and Kafka Services
SSE-Kafka provides a seamless bridge between event-driven Kafka systems and HTTP-based SSE clients, eliminating the need for complex polling mechanisms.
Delivering Kafka Messages to Large-Scale Consumer Groups
It enables efficient, scalable message delivery to multiple SSE clients, ensuring real-time updates without overwhelming Kafka brokers.
Examples
Access the SSE Kafka example files here: SSE Kafka Repository
Full SSE kafka zilla.yaml Config
---
name: example
vaults:
my_servers:
type: filesystem
options:
keys:
store: tls/localhost.p12
type: pkcs12
password: ${{env.KEYSTORE_PASSWORD}}
bindings:
north_tcp_server:
type: tcp
kind: server
options:
host: 0.0.0.0
port:
- 7143
- 7114
routes:
- when:
- port: 7143
exit: north_tls_server
- when:
- port: 7114
exit: north_http_server
north_tls_server:
type: tls
kind: server
vault: my_servers
options:
keys:
- localhost
sni:
- localhost
alpn:
- http/1.1
- h2
exit: north_http_server
north_http_server:
type: http
kind: server
options:
access-control:
policy: cross-origin
routes:
- when:
- headers:
:scheme: http
:authority: localhost:7114
:path: /events
- headers:
:scheme: https
:authority: localhost:7143
:path: /events
exit: north_sse_server
- when:
- headers:
:scheme: http
:authority: localhost:7114
- headers:
:scheme: https
:authority: localhost:7143
exit: east_http_filesystem_mapping
east_http_filesystem_mapping:
type: http-filesystem
kind: proxy
routes:
- exit: east_filesystem_server
when:
- path: /{path}
with:
path: ${params.path}
east_filesystem_server:
type: filesystem
kind: server
options:
location: /var/www/
north_sse_server:
type: sse
kind: server
exit: north_sse_kafka_mapping
north_sse_kafka_mapping:
type: sse-kafka
kind: proxy
routes:
- when:
- path: /{topic}
exit: north_kafka_cache_client
with:
topic: ${params.topic}
north_kafka_cache_client:
type: kafka
kind: cache_client
exit: south_kafka_cache_server
south_kafka_cache_server:
type: kafka
kind: cache_server
options:
bootstrap:
- events
exit: south_kafka_client
south_kafka_client:
type: kafka
kind: client
options:
servers:
- kafka:29092
exit: south_tcp_client
south_tcp_client:
type: tcp
kind: client
telemetry:
exporters:
stdout_logs_exporter:
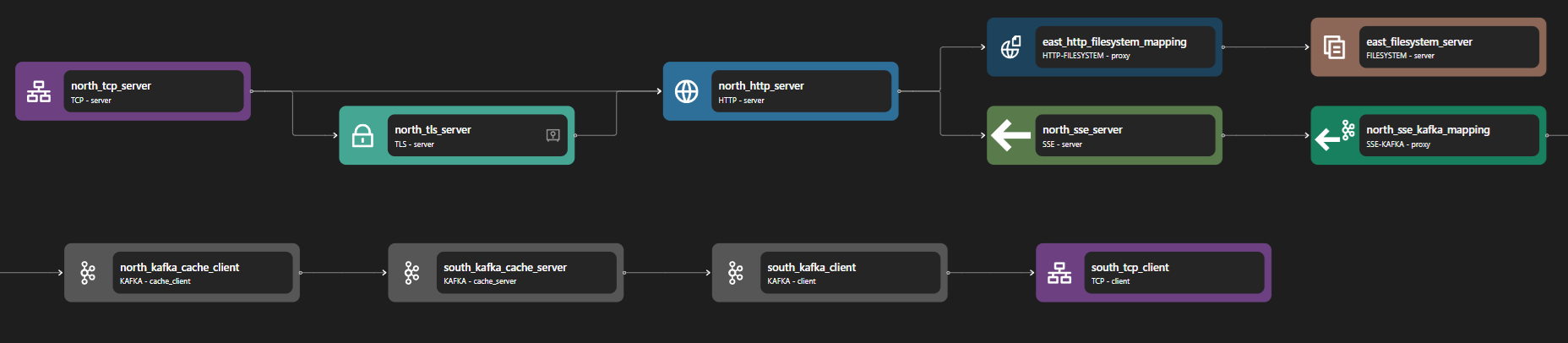
type: stdoutThe above configuration is an example of an SSE Kafka. It listens on HTTP port 7114 or HTTPS port 7143 and will stream back whatever is published to the events topic in Kafka.
The SSE Kafka Proxy can be constructed with three parts: the SSE server, the SSE-Kafka adapter, and the Kafka client. When the SSE server receives a request, the stream is passed into an SSE-Kafka adapter and then converted into a Kafka request.
The SSE server consists of the following bindings: TCP Server, TLS Server, HTTP Server, and SSE server. A TCP Server is required to open a specific port and allow inbound connections. A TLS server is optional but can be used to perform TLS encryption for HTTPS. The data stream is then passed to an HTTP server, which is also passed to an SSE server.
Note
Even though SSE is part of HTTP, it needs a separate binding layer on top of HTTP in Zilla.
The Kafka client consists of the following bindings: Kafka Cache Client, Kafka Cache Server, Kafka Client, and TCP Client. A TCP client is required to allow outbound TCP connections and a Kafka Client is used to connect to external Kafka services. Kafka Cache Client and Server are used for additional layers before direct connection to the Kafka client. These bindings add a caching layer and additional features to Kafka requests through Zilla.
The SSE-Kafka adapter is used to convert SSE-based requests into Kafka-based requests.
Other Examples:

